Dyspnea, otherwise known as abnormal breathing rate, is an uncomfortable symptom, not necessarily a silent medical condition, and can be the result of numerous different underlying medical conditions.
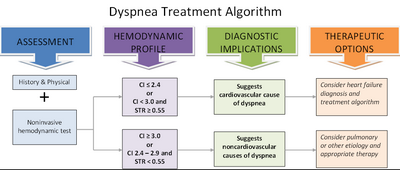
It is very common in the elderly, for example, and affects over 50% of elderly patients seen in the emergency room.
As stated, it is not a disease in its own right, but a symptom of a chronic disease process. The symptoms include breathlessness, chest pain, wheezing, coughing, choking, discomfort during and after sleep, and feeling tired throughout the day. Dyspnea may present itself as a mild or severe case and may include one or more of these symptoms. However, the most common cause is sleep apnea.
Sleep apnea is characterized by pauses in breathing that usually last from five seconds to ten seconds. While pauses may occur spontaneously, or due to an obstruction, the most common causes are stress, anxiety, fatigue, alcohol, or drugs.
People who suffer from sleep apnea may have no clear reason, but certain medical conditions can make it worse, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or heart problems. People with cardiac dysfunction are at a greater risk of having sleep apnea than others. If you are experiencing any of the above symptoms, seek treatment right away to prevent the condition from progressing.
In order to determine if your symptoms are caused by sleep apnea, a physician will need to look at your medical history and conduct an examination. Your doctor will evaluate your breathing habits, check for other respiratory disorders, and examine your skin. A physician will also ask questions about your sleep habits. This exam will be done in order to rule out sleep apnea and other diseases.
Sleep apnea can also cause other symptoms that can range from headaches to abdominal pain, nausea, dizziness, depression, and muscle pain. These symptoms can make it difficult to get a restful night’s sleep. If you don’t sleep well at night, you may find yourself waking up tired throughout the day and being less productive at work and at home.
The definition of dyspnea can vary based on the person who has it. Although there is a list of symptoms and possible causes that the American Dyspnea Association offers, there may be a variety of reasons that a doctor does not conclude that the patient is suffering from sleep apnea, such as a lack of symptoms, or other respiratory conditions.
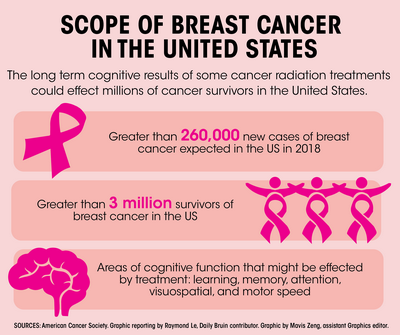
This list of possible symptoms and causes can change over time. The most important point, however, is that symptoms and causes should be identified.
Sleep apnea can occur for a long time without being diagnosed. Because of this, it can become a lifelong problem, even though there are ways to treat the problem. There are many medications available that can treat the underlying health condition that may have contributed to the dyspnea.
Medical experts believe that there are two types of dyspnea – central and obstructive. In both cases, the condition occurs when the airway becomes blocked while sleeping. In most cases, the airway can be opened, but it will either remain obstructed or open slightly and cause difficulty breathing.
There are several different treatments available for both forms of the disorder. The most common treatment for obstructive sleep apnea is a CPAP machine. It can be an effective treatment for patients who suffer from mild dyspnea and those who can’t afford or use more expensive treatments.
If you are looking for treatment for central dyspnea, you may be able to use an appliance called a chin strap. This is similar to a mask worn to help keep the mouth closed during sleep. It provides air and pressure relief by supporting the face to keep the airway open and preventing obstructions.
Another option for treatment is called a continuous positive airway pressure device, or CPAP, which is usually worn overnight. The device is designed to provide pressure to the airway during the night while asleep. It is worn while the patient sleeps and left on during the day. This can be helpful for those who are tired, have a hard time falling asleep, or for people who cannot fall asleep at night due to allergies or poor immune systems.