Treatment options for condyloma acuminatan patients vary widely. The condition may be left untreated if lesions are not symptomatic, or in children and young adults. In symptomatic patients, treatment should be considered, as the condition usually heals without any treatment. In women, however, treatment is often necessary, especially for cosmetic purposes. Available treatments include topical agents, cryotherapy, and surgical excision. The type of procedure used will depend on the morphology of the lesion, the location, and the patient’s preferences.
Although condyloma acuminatan is generally asymptomatic, it is possible to experience pain or bleeding, or psychological distress if left untreated. Female gynecologists can detect the condition during routine examinations of the genital tract. In addition to the anogenital area, it may also occur in the oral cavity. In women, condyloma acuminan can be caused by fomites.
HPV infection is a major cause of condyloma acuminatan. More than one-third of the ninety HPV types infect the genital tract. In addition to condyloma, the disease can lead to dysplasia, an invasive form of cervix cancer, and latent infection. Most condylomata acuminata contain HPV types 6 or 11, though sometimes HPV types 16 are detected. Because HPV type 16 is associated with high recurrences and a higher risk of dysplasia, it may be associated with an increased risk of genital warts.
In most cases, condyloma acuminatan patients are asymptomatic. In some cases, they may experience pain, bleeding, or pruritus. In severe cases, patients may require multiple courses of treatment, and many recur. For those with severe disease, surgical methods are the only options. For those with condyloma, the only way to get rid of it is through an invasive procedure.
The most common condyloma acuminatan types are characterized by their smooth papillary projections. The lesions of women are more common with condyloma acuminan types than men. In women, pearly penile papules are more often visible and can be differentiated from condyloma in men by their vascular coloring and texture.
In general, condyloma acuminatan types are asymptomatic. In some cases, they may be symptomatic. In some patients, the lesions may bleed and cause pain. Some patients have no symptoms or may have a low-grade fever. But other condyloma types can be asymptomatic.
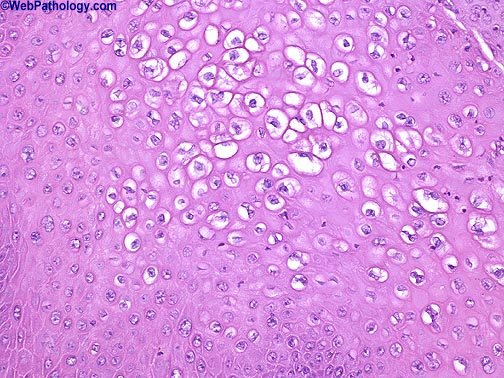
In general, condyloma acuminatan types are asymptomatic, but occasionally they can cause pain, bleeding, or psychological distress. The disease is most commonly diagnosed during a routine female gynecological examination. These types are generally found in the anogenital area, but they may also occur in the oral cavity and mouth. In some cases, the lesions may be caused by a fecal infection.
The occurrence of genital warts is common among adults in the United States. A study conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 1999–2004 found that the number of cases of genital warts increased from the 1960s to 2009. It is important to seek medical attention if lesions cause discomfort.
Most cases of genital warts are associated with HPV types 6 and 11. Although the risk of recurrence for these types is relatively low, the recurrence rate is high, and patients with weakened immune systems may need several courses of treatment before their disease resolves. As with any cancer, it is important to get the diagnosis right. While surgery is usually the primary treatment for genital warts, it may not be suitable for patients with this condition.
Most foci of genital warts have several types of HPV. Of these, more than half of the cases were high-risk HPV. In addition, the two most common types of HPV are present in the disease. This type of cancer is often associated with a number of different underlying factors. The underlying causes of the condition are unknown, but visit https://www.eljolgoriocultural.org.mx/
for more information on the symptoms and treatment of this condition. A person infected with the HPV virus can have one of two diseases.
Various studies have examined the occurrence of the disease. In women with warts, HPV infection is often the underlying cause. There are two types of this virus: the genital variant and the sex type. This last type is most likely infected with a virus. It’s not atypical, but he has an unusual set of chromosomes, which is unusual.