Splenomegaly is an unusual type of growths on the larynx, the voice box, or throat
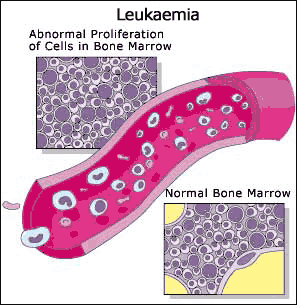
Some of the common causes for splenomegaly are: Haematopoietic diseases: Conditions like leukemia, myeloma, or lymphomas can cause cancerous cells to invade the bone and/or the blood vessels in the splenic fluid and thus enlarge the scenic space. Since the bone has a large mass, it often forms a splenic mass, making it susceptible to splenomegaly invasion.
Bone tumors are the most frequent of all bone abnormalities, affecting about one percent of all cases. In these cases, the bone tumor is located deep within the bone (osteogenic bone tumor). The bone tumor usually causes no symptoms, but it can become enlarged and become cancerous.
Sometimes, however, even the smallest bone abnormality can become an osteogenic bone tumor. These tumors grow slowly, and they are not painful, but they can cause significant damage to the bone because of their very slow growth rate.
The most common cause of splenic involvement with a bone tumor is a haematopoietic abnormality called hematoxyloma. This abnormality is generally associated with hematologic cancers and is a tissue-destroying cancer cell that invades the bone marrow. A cancerous cell in the bone marrow cannot be properly metabolized by the body and becomes a solid. This causes the bone to contract, causing a splenic mass.
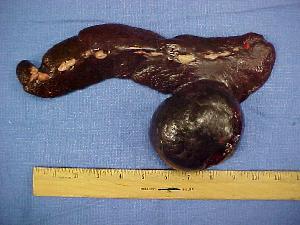
Other causes for splenic involvement with bone tumors include the following: Pericarditis: This condition causes bleeding from the heart to the lungs and to the diaphragm. It results in the swelling of the bone lining (osteolysis) on the outside of the heart or on the surface of the diaphragm, which can produce a bulge in the chest wall, making it difficult for the diaphragm to open and close, and causing splenic involvement with bone tumors.
Pelvic inflammatory disease: Pelvic inflammatory disease can also be a factor in splenic involvement with bone tumors. This condition occurs primarily due to pelvic inflammatory disease, which is a chronic inflammation of the vagina or vulva; it can also be caused by infection of the ovaries or the uterus; inflammation of the bladder may also cause a bulge in the chest wall.
Ureterocele: This is a collection of fluid that collects in the abdomen between the lower and upper ureter. Ureters can sometimes be damaged, forming a bulge in the abdomen.
Sometimes splenic involvement with bone tumors can be a result of other abnormalities such as hypothyroidism or an adrenal tumor. Hypothyroidism can cause the thyroid gland to secrete excessive thyroid hormone, which can lead to a rapid growth of bone in areas surrounding the gland, resulting in a bulge in the abdominal wall.