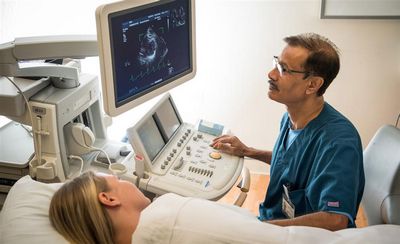
An echocardiogram, heart ultrasound or simply an echo sound, an echocardial scan or an echocardial echo, is a medical imaging study of the heart’s interior.

The use of an endoscope is very useful in diagnosing diseases of the cardiovascular system, such as coronary heart disease and cardiac arrhythmia, which affects many millions of Americans at some time during their lives.
This medical equipment can help detect abnormalities that are difficult to see with the naked eye and can determine if a heart condition or symptom is present before it becomes serious. There are several types of echocardiograms available today, including transvaginal, chest and abdominal.
The most commonly used type of endoscopy is a transvaginal one, which involves inserting a thin, flexible probe through the vagina into the abdominal cavity. Chest and abdominal ones use a small camera that can be placed directly on the chest wall for detailed imaging, while the transvaginal probe is designed to be placed directly on the outside of the vaginal canal.
Other forms of endoscopy include electrocardiograph (ECG) or electrocardiography (EKG), both of which can be performed with the aid of an electronic hearing aids. The results are recorded in the form of a normal pulse pattern. Another type of echosound, the electrocardiogram, involves measuring the electrical activity of the heart, while the echocardial echo is used to look inside the body cavities and determine where the heart is.
An echograph uses sound waves that stimulate the heart to produce a heart rhythm. The term “echosound” comes from the Greek words “echos” meaning “sound”ton” meaning “heart”. When done properly, the waves produce an electronic signal that the patient can hear on the monitor and then interpret as their heart’s beat begins to beat.
Echospectomy can be subdivided into different types.
A simple type is a cutout, which just removes the inner part of the echoscula. A more complicated method is known as the open echospectomy, which also involves removing the tissue surrounding the echoscula and the internal structures.
Echoscopes have different uses for different patients. The most common use is for patients who suffer from coronary heart disease, because the results allow doctors to know if there are any structural abnormalities of the heart and whether they are capable of causing serious problems. If the patient’s heart is beating abnormally, it is possible that it may have a problem.
The results are also helpful in diagnosing cardiac arrhythmia, or a heart condition that affects the rhythms of the heartbeat by producing irregular heartbeats. Another example of a cardiovascular disease that may be identified using an endoscope is in patients who are experiencing a congestive heart failure, a condition wherein the flow of blood in the body is decreased due to lack of oxygen. Anemia may also be diagnosed if the patient’s heart is not working correctly, since it will show a decreased number of red blood cells being pumped throughout the body.
Echocardiography may also be used in patients who suffer from kidney stones. If there is a problem in the kidney’s filtering system, a person may have to undergo surgery to remove the stone or its deposit.
If the stone is small, it may pass through the kidneys without too much trouble, but if it is too large or hard to pass through them, the patient may need to undergo surgery.
One of the most common uses for echocardiography is in the treatment of patients with congenital heart disease. It helps to diagnose the condition, thus enabling doctors to treat it. There are several conditions that an echocardiographer can use to examine the heart. One of the most common of these conditions is ventricular fibrillation, or VF, which causes the heart to pump irregularly through the body’s organs.
This condition may be present at birth or it may be discovered later in life, since the condition may develop over time. Patients suffering from VF are usually monitored closely and regularly given medication to help slow down the heart rate and pump the body’s vital organs more efficiently.
Another condition that may be diagnosed through an echocardiography is called valvular heart disease, which affects the heart valves. This is caused by a build up of plaque, or calcification, in the walls of the heart valve. An electrocardiogram may show whether this condition is present, because the echocardiogram detects the buildup of calcium deposits in the heart muscle. If VF is present, doctors may decide to perform a procedure called a stent placement in order to improve blood flow to the heart muscle.