Anticholinergics are substances which block the action of acetylcholine in neurotransmitters in the nerve and, in general, the nerve center.
They are used for several ailments, the most common of which is Asperger’s syndrome. In most cases, anticholinergics may not have any side effects, although they can cause the presence of drowsiness, fatigue, and depression in some patients.
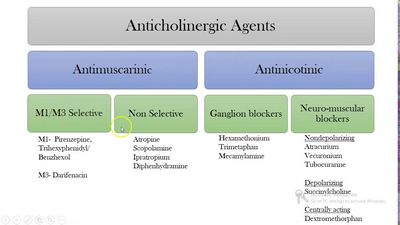
There are two forms of anticholinergics – non-competitive anticholinergics, which are used for treatment of two types of cholinergic symptoms – ataxia, which affect both the motor and sensory neurons, and seizures, which affect only the sensory neurons. Non-competitive anticholinergics include diphenhydramine, levetiracetam, and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs). The most commonly used competitive anticholinergics are atypical antipsychotic medications such as clozapine, olanzapine, and risperidone. They are used for treatment of acute and chronic anticholinergic symptoms.
Anticholinergics work by decreasing the activities of neurotransmitters in the brain and spinal cord. For example, levetiracetam, the most commonly prescribed anticholinergic, blocks acetylcholinesterase (a chemical reaction that breaks down acetylcholine in the brain) by increasing the concentration of serotonin in the synapse. In this way, the acetylcholine receptor on the transmitter cells of the brain are rendered inactive, which in turn, decreases the activity of neurons.
Anticholinergics may be used individually or in combination with another form of therapy. Antidepressants, such as tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), are often used with anticholinergics, particularly when the patient is not responding to other medications or when the side effects of anticholinergics are interfering with the effectiveness of antidepressant therapy. TCAs, such as clomipramine, are often used in combination with anticholinergics to treat mild symptoms of ataxia and dyskinesia. In severe cases of neuroleptic arthritis, for instance, antidepressants can also be used in conjunction with an anticholinergic drug to help reduce the number of relapses of nerve damage.
Other than these types of anticholinergics, other drugs which are used in combination with anticholinergics include anti-anxiety drugs (NSAIDs), which are given to relieve symptoms of pain, such as arthritis and migraine headaches. Although NSAIDs are rarely reported to cause side effects in most patients, there have been reports that some of them, such as ibuprofen, may interact with the anticholinergic drugs for some patients, particularly in terms of possible interactions with tricyclic antidepressants.
Anticholinergics can also be used for treatment of symptoms of depression, including anxiety and panic attacks. If an anticholinergic drug is used in conjunction with depression medication, it can result in a decrease in the effectiveness of one or the other medication and may even cause the depression to worsen.
Anticholinergics are not without risk and should not be used excessively. Anticholinergics are known to have adverse effects on kidney function and can increase the risk of kidney failure. Even if an overdose has no ill effect, it can still lead to withdrawal and death.
Patients who take anticholinergic drugs should avoid driving, operating heavy machinery, using or handling firearms, or performing any other potentially hazardous tasks until their drug therapy has been completed for a reasonable period of time. If you or someone you know has anticholinergic drug-related side effects, seek medical attention right away.
Side effects of anticholinergics include drowsiness, confusion, decreased consciousness, increased heartbeat, muscle weakness, seizures, breathing difficulties, and diarrhea. You may also experience changes in vision, hearing, and taste, skin rash or itching, and vomiting.
As stated previously, anticholinergic drugs can also cause serious side effects. Some of the most serious side effects include coma, seizures, respiratory arrest, seizures, liver failure, kidney failure, hypoglycemia, hyperactivity, and even death.
If you or someone you know is taking anticholinergic drugs, check with your doctor as soon as possible for any serious side effects that may occur. If any serious symptoms appear, you should contact your doctor right away. It is best to seek treatment as soon as possible. If you experience any symptoms while on treatment, your doctor may recommend a hospital stay, but will not necessarily prescribe an IV or intravenous substance.
To prevent serious side effects, it is always a good idea to ask your doctor about all possible drug interactions before starting treatment. This is especially true when combining different drugs.